- 트랜잭션이 반드시 지켜야하는 4가지 특성
Atomicity(원자성)
- 트랜잭션의 모든 작업이 전부 수행되거나(All), 전혀 수행되지 않아야 함(None)
- 중간에 일부만 반영된 상태가 있으면 안 됨
- 예: 계좌 이체
- A → B 송금할 때 A 계좌에서 돈이 빠지고 B 계좌에 입금이 동시에 완료되어야 함
- A에서만 돈이 빠지고 B에 입금 안 되면 원자성이 깨짐 → 롤백 필요
Consistency(일관성)
- 트랜잭션이 수행된 후에도 DB의 무결성 제약 조건이 항상 만족되어야 함
- 즉, 데이터베이스는 유효한 상태에서 또 다른 유효한 상태로만 변해야 함
- 예: 은행 계좌 시스템
- 전체 계좌 잔액 합계가 트랜잭션 전후로 동일해야 함
- 한쪽 계좌에서 빠진 만큼 다른 쪽에 반드시 더해져야 함
Isolation (고립성, 격리성)
- 동시에 실행되는 트랜잭션들이 서로에게 영향을 미치지 않아야 함
- 다른 트랜잭션이 진행 중인 데이터를 읽거나 변경하지 못하게 해야 함
- 이를 보장하기 위해 DB는 격리 수준(Isolation Level)을 제공 (예: Read Committed, Serializable 등)
- 예:
- A가 상품 구매 중인데 B가 동시에 그 상품 재고를 수정하면 데이터 불일치 발생 가능 → 격리 필요
Durability (지속성, 영속성)
- 트랜잭션이 성공적으로 커밋되면, 그 결과는 DB에 영구히 반영되어야 함
- 시스템 장애, 전원 꺼짐, 서버 다운이 발생해도 데이터가 보존되어야 함
- DB는 이를 위해 로그 기록 (Write-Ahead Logging, WAL) 등을 사용
정리
- A == 원자성이며 All or Nothing
- C == 일관성이며 무결성 규칙 항상 유지
- I == 고립성이며 트랜잭션 간 간섭 방지
- D == 지속성이며 커밋된 데이터는 영구 저장
코드로 한 번 실행해보자
entity
package com.springboot.transaction.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
@Entity
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Account {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true, length = 50)
private String owner;
@Column(nullable = false, precision = 19, scale = 2)
private BigDecimal balance;
@Version
private Long version; // 낙관적 락(동시성 안전을 조금 더 확보)
public Long getId() { return id; }
public String getOwner() { return owner; }
public BigDecimal getBalance() { return balance; }
public Long getVersion() { return version; }
public void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) {
if (amount.signum() <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("amount must be positive");
BigDecimal next = this.balance.subtract(amount);
if (next.signum() < 0) throw new IllegalStateException("잔액 부족");
this.balance = next;
}
public void deposit(BigDecimal amount) {
if (amount.signum() <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("amount must be positive");
this.balance = this.balance.add(amount);
}
protected Account() {}
public Account(String owner, BigDecimal balance) {
this.owner = owner;
this.balance = balance;
}
}
controller
package com.springboot.transaction.controller;
import com.springboot.transaction.dto.AccountDto;
import com.springboot.transaction.entity.Account;
import com.springboot.transaction.repository.AccountRepository;
import com.springboot.transaction.service.TransferService;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/api/accounts")
public class AccountController {
@Autowired
private AccountRepository accountRepository;
@Autowired
private TransferService transferService;
@PostMapping("/init")
public ResponseEntity<?> init() {
transferService.init("alice", new BigDecimal("100000"), "bob", new BigDecimal("50000"));
return ResponseEntity.ok(Map.of("ok", true));
}
@GetMapping("/select")
public List<AccountDto> list() {
return transferService.findAllAccounts();
}
@PostMapping("/transfer")
public ResponseEntity<?> transfer(@RequestBody TransferRequest req) {
transferService.transfer(req.from(), req.to(), req.amount(), req.makeError());
return ResponseEntity.ok(Map.of("ok", true));
}
public record TransferRequest(String from, String to, BigDecimal amount, boolean makeError) {}
}
service
package com.springboot.transaction.service;
import com.springboot.transaction.dto.AccountDto;
import com.springboot.transaction.entity.Account;
import com.springboot.transaction.repository.AccountRepository;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class TransferService {
@Autowired
private AccountRepository accountRepository;
/** Atomicity/Isolation를 체감하기 위한 계좌 이체 */
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED) // 기본값 명시(학습용)
public void transfer(String fromOwner, String toOwner, BigDecimal amount, boolean makeErrorAfterDeposit) {
Account from = accountRepository.findByOwner(fromOwner)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("출금 계좌 없음: " + fromOwner));
Account to = accountRepository.findByOwner(toOwner)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("입금 계좌 없음: " + toOwner));
// 비즈니스 규칙(Consistency 보장의 일부)
if (fromOwner.equals(toOwner)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("동일 계좌 이체 불가");
from.withdraw(amount);
to.deposit(amount);
// 더티체킹으로 커밋 시점에 update 발생
// 의도적으로 에러를 던져 롤백(원자성) 확인
if (makeErrorAfterDeposit) {
throw new RuntimeException("테스트용 강제 예외 → 전체 롤백되어야 함");
}
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public List<AccountDto> findAllAccounts() {
return accountRepository.findAll()
.stream()
.map(AccountDto::fromEntity) // Entity → DTO 변환
.toList();
}
/** 테스트용 초기화 */
@Transactional
public void init(String aOwner, BigDecimal aBal, String bOwner, BigDecimal bBal) {
accountRepository.findByOwner(aOwner).orElseGet(() ->
accountRepository.save(new Account(aOwner, aBal)));
accountRepository.findByOwner(bOwner).orElseGet(() ->
accountRepository.save(new Account(bOwner, bBal)));
}
}repository
package com.springboot.transaction.repository;
import com.springboot.transaction.entity.Account;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface AccountRepository extends JpaRepository<Account, Long> {
Optional<Account> findByOwner(String owner);
}
dto
package com.springboot.transaction.dto;
import com.springboot.transaction.entity.Account;
import lombok.Getter;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
@Getter
public class AccountDto {
private Long id;
private String owner;
private BigDecimal balance;
public AccountDto() {} // 기본 생성자
public AccountDto(Long id, String owner, BigDecimal balance) { // 모든 필드 생성자
this.id = id;
this.owner = owner;
this.balance = balance;
}
public Long getId() { return id; }
public String getOwner() { return owner; }
public BigDecimal getBalance() { return balance; }
// 엔티티 → DTO 변환
public static AccountDto fromEntity(Account account) {
return new AccountDto(
account.getId(),
account.getOwner(),
account.getBalance()
);
}
}
- 이걸로 데이터 만들기
<http://localhost:8080/api/accounts/init>
- 데이터 조회
<http://localhost:8080/api/accounts/select>
결과
[
{
"id": 1,
"owner": "alice",
"balance": 100000.00
},
{
"id": 2,
"owner": "bob",
"balance": 50000.00
}
]
<http://localhost:8080/api/accounts/transfer>
- 이 api를 본다면 계좌 이체 API 엔드 포인트이다.
클라이언트에서
- from → 출금 계좌 소유자
- to → 입금 계좌 소유자
- amount → 이체 금액
- makeError → true면 강제로 예외 발생 == 롤백 확인용
{
"from": "alice",
"to": "bob",
"amount": 20000,
"makeError": false
}
초기값

A — Atomicity (원자성)
- 아까 위에서 봤을 때 트랜잭션 경계 안의 작업은 전부 성공하거나(Commit) 전부 실패(전부 Rollback) 해야한다.
- 라는 것이다. 먼저 Service 코드 부터 보면
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED) // 기본값 명시(학습용)
public void transfer(String fromOwner, String toOwner, BigDecimal amount, boolean makeErrorAfterDeposit) {
Account from = accountRepository.findByOwner(fromOwner)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("출금 계좌 없음: " + fromOwner));
Account to = accountRepository.findByOwner(toOwner)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("입금 계좌 없음: " + toOwner));
// 비즈니스 규칙(Consistency 보장의 일부)
if (fromOwner.equals(toOwner)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("동일 계좌 이체 불가");
from.withdraw(amount);
to.deposit(amount);
// 더티체킹으로 커밋 시점에 update 발생
// 의도적으로 에러를 던져 롤백(원자성) 확인
if (makeErrorAfterDeposit) {
throw new RuntimeException("테스트용 강제 예외 → 전체 롤백되어야 함");
}
}
1. Transcational 메서드 안에 from.withdraw, to.deposit이 둘 다 성공해야 커밋이 됨
public void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) {
if (amount.signum() <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("amount must be positive");
BigDecimal next = this.balance.subtract(amount); // 잔액 - 출금액
if (next.signum() < 0) throw new IllegalStateException("잔액 부족");
this.balance = next;
}
public void deposit(BigDecimal amount) {
if (amount.signum() <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("amount must be positive");
this.balance = this.balance.add(amount);
}
2. 도중 예외
- 잔액 부족 또는 RuntimeException가 던져지면 전체 롤백
// 더티체킹으로 커밋 시점에 update 발생
// 의도적으로 에러를 던져 롤백(원자성) 확인
if (makeErrorAfterDeposit) {
throw new RuntimeException("테스트용 강제 예외 → 전체 롤백되어야 함");
}
위를 실행시키면 결과
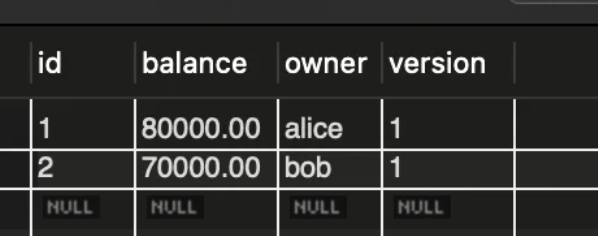
여기서 의문인 거는 save를 안했는데 자동 저장됨
JPA의 영속성 컨텍스트(persistence context) + 더티 체킹(dirty checking)
- 이거 덕분에 save를 하지 않아도 자동적으로 실행됨
Account from = accountRepository.findByOwner(fromOwner).orElseThrow(...);
- JPA가 위를 실행한 후 Account 엔티티는 연속성 컨텍스트(EntityManager 1차 캐시)에 저장됨
- 즉 DB와 연결된 관리되는 상태
from.withdraw(amount);
- 자바 객체의 balance 필드값(돈)을 바꾸는 것 뿐
- 아직 update SQL은 실행되지 않음 하지만 JPA가 영속성 컨텍스트 안에서 “이 엔티티의 값이 바뀌었다”를 기록해둠
to.deposit(amount);
- 자바 객체 필드만 변경됨
- 영속성 켄텍스트가 “변경된 스냅샷”을 계속 추적
트랜잭션 종료 시점(@Transactional)
- @Transactional 때문에 Spring이 트랜잭션을 시작/종료 관리
- 메서드가 정상 종료 → 스프링이 commit 호출
- 그 순간 Hibernate(JPA 구현체)가 영속성 컨텍스트의 “변경된 엔티티 목록”을 확인 → DB에 UPDATE SQL을 실행
update account set balance=?, version=? where id=? and version=?;
→ 이게 바로 더티 체킹 == 자바 객체를 바꿨는데 JPA가 알아서 DB에 반영해줌
@Transactional이 붙은 메서드가 끝나고 commit될 때 JPA가 자동으로 flush()하면서 발생
여기서 이제 왜 All-or-nothing?
💡
- JPA는 트랜잭션 커밋 시점에 엔티티 변경을 감지(더티 체킹)해 UPDATE SQL을 내보낸다
- 예외가 나면 스프링이 현재 트랜잭션을 rollback-only 로 표시하고 실제로 롤백해 두 계좌의 변경이 모두 취소 </aside>
여기서 중요한 것은
- 런타임 예외 (RuntimeException과 그 하위, 예: NullPointerException, IllegalStateException …)
- 👉 롤백됨
- 체크 예외 (Exception이지만 RuntimeException이 아닌 것, 예: IOException, SQLException)
- 👉 롤백되지 않고 커밋됨
이렇게 만든 이유는
- 런타임 예외는 대부분 “프로그래밍 오류/데이터 무결성 문제” → 회복 불가 → 롤백하는 게 안전
- 체크 예외는 보통 “외부 리소스 문제” (예: 네트워크 오류, 파일 읽기 실패) →
- 개발자가 직접 잡아서 처리할 수 있도록 두는 게 합리적 → 롤백 안 함
스프링은 안전하게 하기 위해 RuntimeException만 자동 롤백하도록 설계한 것임
C — Consistency (일관성)
- 트랜잭션 전/후로 데이터는 유효한 상태(무결성 제약)를 지켜야 한다
코드에서는
@Entity
public class Account {
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true, length = 50)
private String owner;
@Column(nullable = false, precision = 19, scale = 2)
private BigDecimal balance;
public void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) {
if (amount.signum() <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("amount must be positive");
BigDecimal next = this.balance.subtract(amount);
if (next.signum() < 0) throw new IllegalStateException("잔액 부족"); // ← 무결성 수호
this.balance = next;
}
}
- 음수 잔액을 금지
- DB제약에서 @Column(nullable = false, unique = true)→
- owner의 NULL 금지/중복 금지
- balance에 precision/scale 지정
I — Isolation (격리성)
- 동시에 실행되는 트랜잭션끼리 서로의 미완료 변경을 보지 못한다.
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED) // 기본값 명시(학습용)
- @Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED) (기본값과 동일)
→ 커밋된 것만 읽음. 다른 트랜잭션이 아직 커밋하지 않은 변경은 안 보임
@Entity
public class Account {
@Version
private Long version; // ← 동시성 충돌 시 예외 발생 → 트랜잭션 롤백
}
- 이거는 JPA는 update시 자동으로 이 값을 중가시킴 즉 DB 레코드에 버전 번호가 기록되고, 같은 행을 동시에 여러 트랜잭션이 수정할 때 충돌을 감지하는 데 쓰인다.
예를 들어 두 사용자가 동시에 같은 계좌를 불러온다고 했을 때
- 트랜잭션 A: balance=1000, version=1
- 트랜잭션 B: balance=1000, version=1
A가 200원 출금 → 커밋
- JPA는 update 시 아래 SQL을 날립니다:
update account
set balance = 800, version = 2
where id = 1 and version = 1;
성공적으로 반영됨 (버전 1 → 2)
B도 300원 출금 → 커밋 시도
- B가 본 balance=1000, version=1 기준으로 update하려고 합니다:
update account
set balance = 700, version = 2
where id = 1 and version = 1;
- 하지만 지금 DB에는 version = 2라서 조건(version=1)이 안 맞음 → 업데이트된 행이 0개
- JPA가 이걸 감지하고 OptimisticLockException 발생 → 트랜잭션 롤백
이걸 왜 하냐
→ 이걸 안 쓰면 “Lost Update(갱신 손실)” 문제가 발생
- 동시에 읽은 값(1000)을 기준으로 각각 수정하면, 나중에 저장한 값이 앞선 변경을 덮어써버림 → 데이터 손실
- @Version이 있으면 충돌을 감지하고 롤백 → 개발자가 재시도 로직을 작성해서 안전하게 처리 가능
D — Durability (지속성)
- 커밋된 결과는 장애가 나도 사라지지 않는다.
- 서비스 메서드가 정상 종료되면 스프링이 커밋 → JPA가 UPDATE/INSERT → MariaDB(InnoDB)가 로그/디스크에 반영
- 애플리케이션를 재시작해도 데이터가 남아있음(실제로 /select로 다시 확인 가능)
💡 DB 레벨에선 InnoDB의 WAL/redo log 정책에 의해 커밋의 영속성이 보장됨 (학습 포인트로만 기억해두면 충분하다
'개발 지식 > KSUG' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [KSUG Spring Boot Study] Propagation (1) | 2025.08.28 |
|---|---|
| [KSUG Spring Boot Study] 트랜잭션 범위 (Class, Method) (3) | 2025.08.28 |
| [KSUG Spring Boot Study] DAO 연동을 위한 컨트롤러와 서비스 설계 (1) | 2025.08.17 |
| [KSUG Spring Boot Study] DAO 설계 (1) | 2025.08.17 |
| [KSUG Spring Boot Study] 엔티티 설계 - 실습 (0) | 2025.08.17 |


